Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 observation of surface reactions; Present status and future prospects"
observation of surface reactions; Present status and future prospects"Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Hoshako, 35(3), P. 157, 2022/05
Ambient Pressure-XPS [AP-XPS] has been in operation at synchrotron radiation facilities around the world since around 2000 to study gas-surface reactions. Furthermore, it is also applied to observe liquid and solid-liquid interfaces. Development and utilization research is underway as a tool to take the true picture of surface phenomena. A special issue on AP-XPS for the Journal of the Japanese Society for Synchrotron Radiation Research was designed and its purpose is explained.
 observation of surface reactions under the gas atmosphere; History, applications, issues, and future prospect
observation of surface reactions under the gas atmosphere; History, applications, issues, and future prospectTakakuwa, Yuji*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Hoshako, 35(3), p.158 - 171, 2022/05
Ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy for in situ observation of surface reactions using high-brightness synchrotron radiation shows a rapid progress in the number of endstations since about 2005 and is applied to various practical research field for clarifying reactions at solid/gas interfaces of e.g. catalyst, solid/liquid interfaces of e.g. fuel cell, and gas/liquid interfaces of e.g. ion liquid. In this review, a history of the development of APXPS, real-time observation of the surface reactions for Si chemical vapor deposition and Si dry oxidation, issues of APXPS, and future prospects are described.
Toyoda, Satoshi*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*
Hoshako, 35(3), p.200 - 206, 2022/05
The present status of spatiotemporal depth profiling analysis of the multilayer stacked film interface based on Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (APXPS) is presented. To begin with, depth profiles of the multilayer stacked film interfaces have been achieved by time-division Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved PhotoEmission Spectroscopy data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division angle resolved AP-XPS data including spatial resolution, which enables us to realize spatiotemporal depth profiles of the interfaces under reaction conditions such as oxidation and reduction. In addition, it is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
Matsumura, Daiju; Kato, Kazuo*
Hoshako, 34(1), p.3 - 11, 2021/01
no abstracts in English
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Hoshako, 32(4), p.185 - 198, 2019/07
Synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy is a beneficial technique for precise analysis of chemical states of solid surfaces. Owing to its high luminosity, it ensures availability of termed synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy which enables " " observation of chemical reactions with gas molecules occurring at surfaces. In this review, oxygen adsorption reactions in the oxidation of silicon single crystal surfaces are focused. Through the demonstration of our research, the usefulness of synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy to study molecular adsorption reactions at solid surfaces is briefly described and the future perspective would also be shown.
" observation of chemical reactions with gas molecules occurring at surfaces. In this review, oxygen adsorption reactions in the oxidation of silicon single crystal surfaces are focused. Through the demonstration of our research, the usefulness of synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy to study molecular adsorption reactions at solid surfaces is briefly described and the future perspective would also be shown.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Hoshako Riyo No Tebiki, p.130 - 138, 2019/02
The educational book on next-generation synchrotron radiation usage is partially written. This book is being planned by several professors at Tohoku University. In this book, the contents which have already reported in our recent paper [Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 (2018) 021603.] are mainly written. The future perspective on photoemission electron microscopy using next generation synchrotron radiation and its possibility to analyze environmental samples and insulating functional materials are also described.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Shiwaku, Hideaki
Hoshako, 31(4), p.274 - 280, 2018/07
As a method for disposal of nuclear waste, the use of vitrification technique is very promising. In this technique, many kinds of elements should be involved stably in the glass and chemical state of these elements in the glass must be confirmed in order to guarantee stability of the glass. We have used synchrotron based X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) technique, in which the element selectivity is utilized, to obtain the chemical state of each element in many kinds of simulated glass samples. In addition, imaging XAFS technique has been used to clarify correlation between constituent elements. We are going to contribute to research and development of the vitrification technique by using synchrotron radiation based XAFS analyses. In this article, we introduce results of the high energy XAFS of high temperature slag samples, the imaging study of high temperature borosilicate glass samples and the imaging XAFS analysis of platinum group metals in the borosilicate glass samples.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro
Hoshako, 28(3), p.117 - 123, 2015/05
Atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) analysis are the method which visualizes the structure from a short- to middle-range order. It has been applied to amorphous materials and liquids in the past. It could also be used now for the crystallized materials by using a synchrotron X-ray and a pulsed neutron facilities. There is some deviation between the average structure obtained by the traditional crystal structure analysis, and the local structure caused by the domain configuration in ferroelectrics, magnetic materials, hydrogen-storage materials, etc. The PDF analysis is attracted as the method bridging the local and the average structure. The outline of development of research technique and applications are reviewed about the PDF analysis using synchrotron X-ray.
 -
- transition of iron by using EXAFS
transition of iron by using EXAFSIshimatsu, Naoki*; Sata,Yusuke*; Maruyama, Hiroshi*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Sumiya, Hitoshi*
Hoshako, 28(1), p.3 - 11, 2015/01
no abstracts in English
Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Toru; Ikeda, Takashi; Matsumura, Daiju; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki
Hoshako, 27(6), p.315 - 322, 2014/11
no abstracts in English
Ito, Takanori*; Igawa, Naoki; Homma, Tetsuo*
Supuringu-8 No Kokido Hoshako O Riyoshita Gurin Enerugi Bunya Niokeru Denchi Kaihatsu, p.104 - 112, 2014/02
Functional materials consist of many elements and therefore have complex crystal structure. Synchrotron X-ray and neutron scattering facilities are powerful tools to investigate the crystal structural information of those materials. Here we make an introduction to the crystal analysis method by the synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction applying to the solid oxide fuel cells.
 synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction measurement
synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction measurementSaito, Hiroyuki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
Hoshako, 27(1), p.10 - 19, 2014/01
no abstracts in English
Harries, J.; Shigemasa, Eiji*
Hoshako, 26(6), p.327 - 334, 2013/11
We report on the first observation of superfluorescence (collective spontaneous emission) at an FEL, using the EUV free-electron laser and a high number density helium gas cell. We introduce superfluorescence as an example of quantum optics experiments which can be performed at the new generation of light sources, and discuss future prospects, including the extension to shorter wavelengths.
Nishihata, Yasuo; Matsumura, Daiju
Hoshako, 26(2), p.57 - 63, 2013/03
Self-regeneration of the intelligent catalyst as an automotive catalyst was observed by  XAFS. Palladium nano-particles in catalytic reaction were also observed to elucidate the difference in activity between the intelligent catalyst and the conventional one. Copper has been investigated as a candidate to replace precious metals since the first-principle theory predicts an active copper surface for NO dissociation. The redox property of Cu turned into a similar property of precious metals by managing the interaction between Cu particles and a substrate. The conversion efficiency of Ni-Cu alloy particles increased than each element alone. The Ni was oxidized faster than the Cu so as to maintain a metallic surface of Cu. These properties of Cu were incorporated into new design of a Cu catalyst, which has achieved high catalytic activity with the regular operation of engine in the beginning.
XAFS. Palladium nano-particles in catalytic reaction were also observed to elucidate the difference in activity between the intelligent catalyst and the conventional one. Copper has been investigated as a candidate to replace precious metals since the first-principle theory predicts an active copper surface for NO dissociation. The redox property of Cu turned into a similar property of precious metals by managing the interaction between Cu particles and a substrate. The conversion efficiency of Ni-Cu alloy particles increased than each element alone. The Ni was oxidized faster than the Cu so as to maintain a metallic surface of Cu. These properties of Cu were incorporated into new design of a Cu catalyst, which has achieved high catalytic activity with the regular operation of engine in the beginning.
Kono, Hidetoshi; Ikeda, Shiro*
Hoshako, 26(1), p.38 - 43, 2013/01
A new strong, short-pulse and coherent X-ray light source, which has been built at SPring8, is expected to achieve a single molecular imaging. With this 109 times brighter light than that of the current synchrotrons, we have to measure the diffraction within a few femto-second before the molecule is destroyed due to the radiation damage. Thus, the obtained diffraction pattern will be very sparse. We have recently developed a phase retrieval method based on the Bayesian statistics that is applicable for such a sparse diffraction pattern. In this article, we introduce the method.
Watanuki, Tetsu; Kawana, Daichi*; Machida, Akihiko; Tsai, A. P.*
Hoshako, 25(3), p.176 - 183, 2012/05
Quasiperiodic intermediate-valence systems were prepared by applying pressure to Yb-based quasicrystals. In these systems, each quasiperiodic lattice point has a charge degree of freedom. Synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectroscopy experiments near the Yb 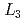 -edge demonstrate that the Yb valence in a Cd-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal increases continuously upon compression from a divalent state at ambient pressure and reaches 2.33 at 31.7 GPa, where the quasiperiodically arranged Yb ions take a valence fluctuation state. For the case of a Cd-Mg-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal, the Yb valence reaches a value of 2.71 at 57.6 GPa. By following the trend of Yb-based intermediate-valence crystalline compounds, this large valence increase suggests that the 4f electron system in this quasicrystal varies from a valence fluctuation regime to a strong correlated electron regime.
-edge demonstrate that the Yb valence in a Cd-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal increases continuously upon compression from a divalent state at ambient pressure and reaches 2.33 at 31.7 GPa, where the quasiperiodically arranged Yb ions take a valence fluctuation state. For the case of a Cd-Mg-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal, the Yb valence reaches a value of 2.71 at 57.6 GPa. By following the trend of Yb-based intermediate-valence crystalline compounds, this large valence increase suggests that the 4f electron system in this quasicrystal varies from a valence fluctuation regime to a strong correlated electron regime.
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.*
Hoshako, 23(5), p.308 - 312, 2010/09
We have characterized the performance of LiF crystal as an imaging sensor for extreme ultraviolet free electron laser (EUV-FEL). We found that the LiF crystal could register a single shot image of various materials in a wide field of view with high spatial resolution and high dynamic range. Detailed structure of focused spot image of single shot EUV-FEL was measured using the LiF crystal. It is found that a crater appears on a surface of LiF in one shot.
Tanaka, Keisuke*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Akiniwa, Yoshiaki*; Shobu, Takahisa
Hoshako Ni Yoru Oryoku To Hizumi No Hyoka, 238 Pages, 2009/10
no abstracts in English
 Mn
Mn As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroismTakeda, Yukiharu; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Okane, Tetsuo; Okochi, Takuo*; Okamoto, Jun*; Saito, Yuji; Kobayashi, Keisuke*; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Tanaka, Arata*; et al.
Hoshako, 22(4), p.202 - 209, 2009/07
no abstracts in English
 Al
Al
Fujimori, Shinichi; Saito, Yuji; Okane, Tetsuo; Fujimori, Atsushi; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika
Hoshako, 22(1), p.11 - 19, 2009/01
We have performed angle-resolved photoemission experiments in soft X-ray region (SX-ARPES) for the heavy Fermion superconductor UPd Al
Al to observe its band structure. At low temperatures (20 K), renormalized quasi-particle bands were observed in the vicinity of the Fermi level. The overall structure of ARPES spectra including strongly dispersive bands on the higher binding energy sides is fairly well explained by the band structure calculation treating U 5f electrons as being itinerant. This suggests that itinerant description is a reasonable approach to understand their electronic properties at low temperatures. On the other hand, at high temperatures (100 K), the quasi-particle bands moved toward higher binding energies, and became less dispersive. This suggests that the U 5f electrons change their character from itinerant one at low temperatures to localized one at high temperatures.
to observe its band structure. At low temperatures (20 K), renormalized quasi-particle bands were observed in the vicinity of the Fermi level. The overall structure of ARPES spectra including strongly dispersive bands on the higher binding energy sides is fairly well explained by the band structure calculation treating U 5f electrons as being itinerant. This suggests that itinerant description is a reasonable approach to understand their electronic properties at low temperatures. On the other hand, at high temperatures (100 K), the quasi-particle bands moved toward higher binding energies, and became less dispersive. This suggests that the U 5f electrons change their character from itinerant one at low temperatures to localized one at high temperatures.